Radon exposure is a significant health concern because it is a radioactive gas that can cause lung cancer. Radon is produced from the natural decay of uranium in soil, rock, and water, and it can accumulate in homes and buildings, especially in confined areas such as basements and crawl spaces. Here’s how uranium levels in hair tissue and urine analysis can point to radon exposure, and why functional medicine testing can be a good idea for individuals exposed to high levels of radon:
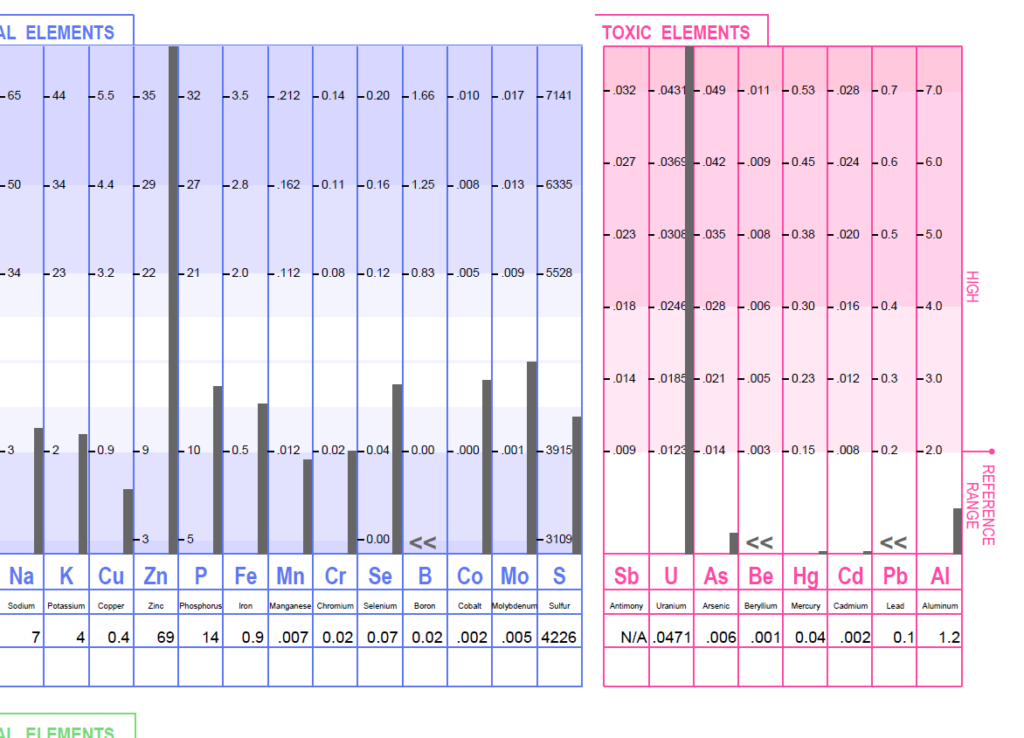
Uranium Levels in Hair Tissue and Urine Analysis
- Radon and Uranium Decay Chain:
- Radon (Rn-222) is part of the uranium-238 decay series. When uranium-238 decays, it produces radium-226, which then decays into radon-222. Radon-222 further decays into several short-lived radioactive progeny (polonium-218, lead-214, bismuth-214, and others).
- These decay products can attach to dust and other particles, which can be inhaled, leading to internal radiation exposure.
- Biological Uptake and Detection:
- Hair Tissue Analysis: Hair can incorporate heavy metals and radioactive isotopes from the bloodstream. Since uranium is a heavy metal, its presence in hair can be an indicator of exposure. Elevated levels of uranium in hair tissue suggest that there has been significant exposure to uranium or its decay products, which can be linked to radon exposure.
- Urine Analysis: Uranium is also excreted through urine. A urine test can detect elevated levels of uranium, indicating recent or ongoing exposure. Since radon exposure often involves the inhalation of its radioactive decay products, which include uranium isotopes, this can be reflected in urine samples.
Connection Between Radon and Uranium Levels
- Inhalation and Ingestion: People living in radon-rich environments may inhale radon and its progeny, which then deposit radioactive particles in the lungs. These particles can then enter the bloodstream and be distributed throughout the body, including to hair and kidneys.
- Radon Progeny: The decay products of radon (e.g., polonium, lead, and bismuth isotopes) can also contribute to internal contamination. These progeny can be detected alongside uranium in biological samples.

Functional Medicine Testing
Functional medicine focuses on identifying and addressing the root causes of disease, often using comprehensive and individualized testing. For someone exposed to high levels of radon, functional medicine testing can be valuable:
- Comprehensive Assessment:
- Functional medicine practitioners can conduct a thorough assessment, including a detailed history of environmental exposures, lifestyle, and genetic predispositions.
- Testing can include hair tissue mineral analysis (HTMA) and urine tests for heavy metals and radionuclides.
- Holistic Approach:
- Functional medicine takes a holistic approach to health, considering the interplay between various systems in the body. This is crucial for understanding the broader impacts of radon exposure.
- Practitioners can recommend detoxification protocols, nutritional support, and lifestyle modifications to mitigate the effects of radon exposure.
- Preventive and Therapeutic Strategies:
- Identifying high levels of uranium and other radioactive elements can prompt immediate actions to reduce exposure, such as improving ventilation, sealing cracks in floors and walls, and using radon mitigation systems.
- Functional medicine can also provide therapeutic strategies to enhance the body’s natural detoxification processes, support immune function, and repair cellular damage caused by radiation.
Conclusion
Detecting uranium levels in hair tissue and urine can serve as important biomarkers for assessing radon exposure. Given the health risks associated with radon, including lung cancer, it is advisable for individuals in radon-prone areas or those with known high radon levels in their environment to undergo functional medicine testing. This comprehensive approach can help in early detection, effective intervention, and long-term health maintenance.
Protect Your Health: Get Tested for Toxic Elements Today!

